A comparison of two anesthesia protocols and effects on stress. Results
Authors: L.V. Brylev, V.V. Fominykh, V.Y. Chernenkaya, I.M. Chernenkaya, K.V. Gorbachev, A.I. Ataulina, A.A. Izvekov, M.M. Monakhov, A.M. Olenichev, S.Y. Orlov, I.N. Tyurin, M.A. Loginov, S.A. Rautbart, A.M. Baimukanov, V.V. Parshikov, V.S. Demeshonok, A.A. Yakovlev,
T.A. Druzhkova, A.B. Geht, N.V. Gulyaeva
Study results published in the Metabolic Brain Disease journal in 2021
Dysphagia and progressive swallowing difficulties as a result of motor neuron death are symptoms of ALS. Malnutrition and weight loss lead to a compromised immune system, fatigue, and an increased risk of infectious complications in ALS patients.
Gastrostomy placement is a widely recognized method for dealing with swallowing difficulties. Gastrostomy tube placement can increase the life expectancy of ALS patients. Despite nutritional correction, there can sometimes be a dramatic progression of neurological deficits after gastrostomy, which may be related to the development of exteroceptive stress (stress caused by an external stimulus) during gastrostomy placement.
It has been suggested that the use of intravenous anesthesia could reduce this stress during surgery, which would increase the safety of gastrostomy in ALS.
The aim of our study: compare two different gastrostomy placement protocols (local anesthesia or local anesthesia plus intravenous anesthesia) in terms of stress load and effect on disease progression.
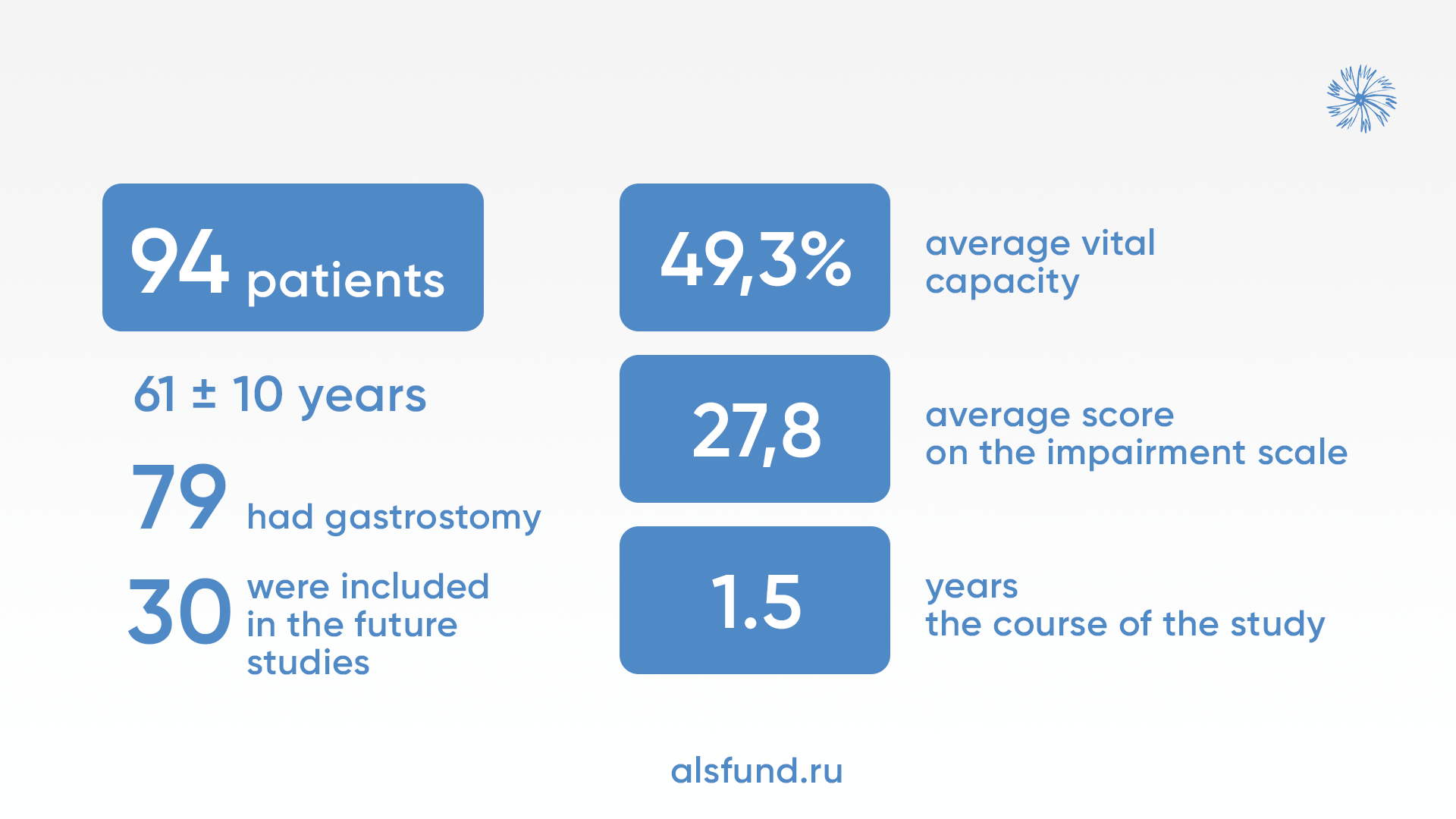
Over the course of 1.5 years, 94 patients participated in the study. Gastrostomy was placed in 79 patients, 30 of them were included in the study according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. All patients were divided into two groups according to the type of anesthesia. Their biochemical parameters, markers of neuronal death, and stress levels were measured.
The age of ALS patients was 61 ± 10 years. Gastrostomy was inserted on average 14 months after diagnosis and about 2.2 years after the first symptoms. The average score on the impairment scale for ALS was 27.8. Average vital capacity was 46.3% (19-91%). The mean life expectancy after gastrostomy placement was 5 months (5 days to 20 months).
High levels of salivary cortisol, serum cortisol, glucose, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 were detected after gastrostomy, which confirms a stress reaction after surgical intervention.
Comparison of the two gastrostomy placement protocols revealed no differences in longevity, stress load, and inflammation.

